RF Connector & Cable
Mastering RF Cable Assemblies
RF cable assemblies are crucial in modern communication systems. As transmission lines for RF signals, they effectively connect various devices and components within the system, such as between PCB boards, between PCB boards and antennas, between devices and antennas, and between devices.
What is an RF cable assembly?
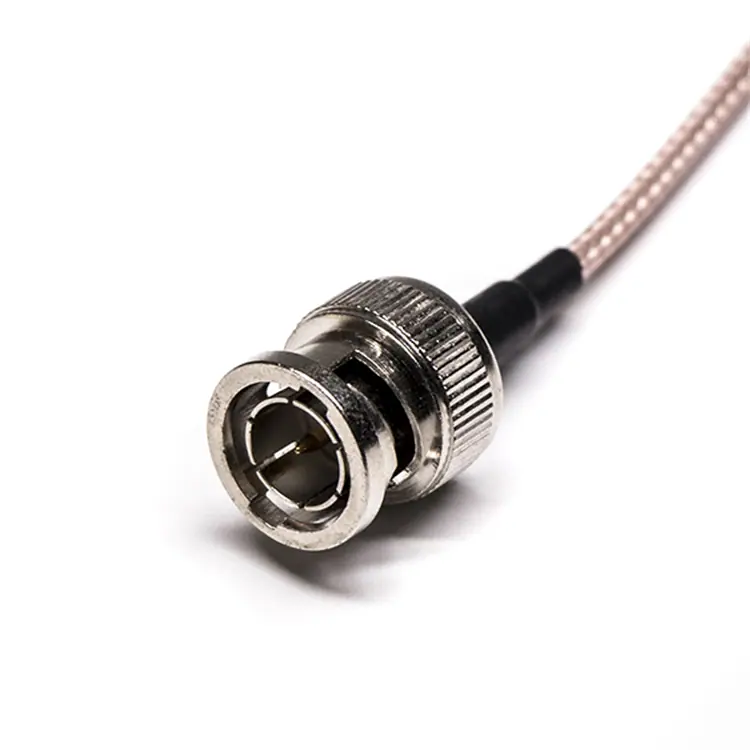
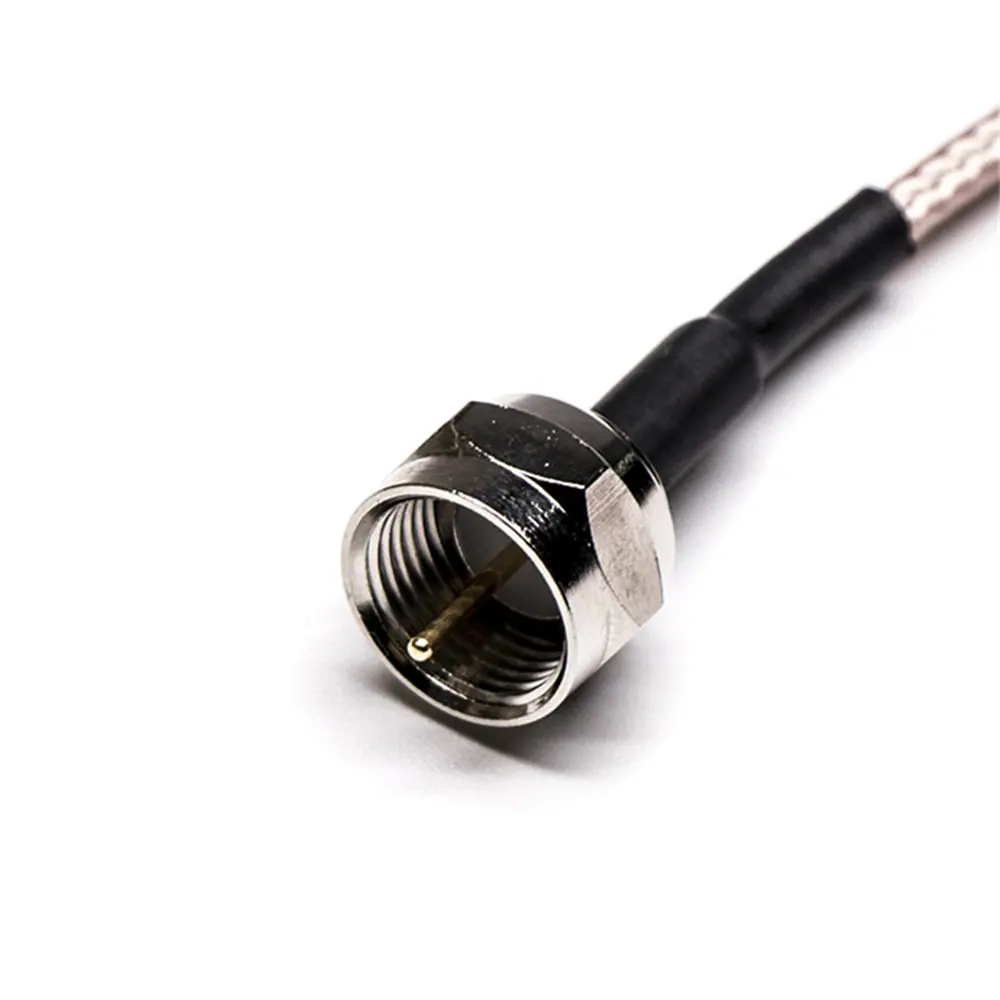
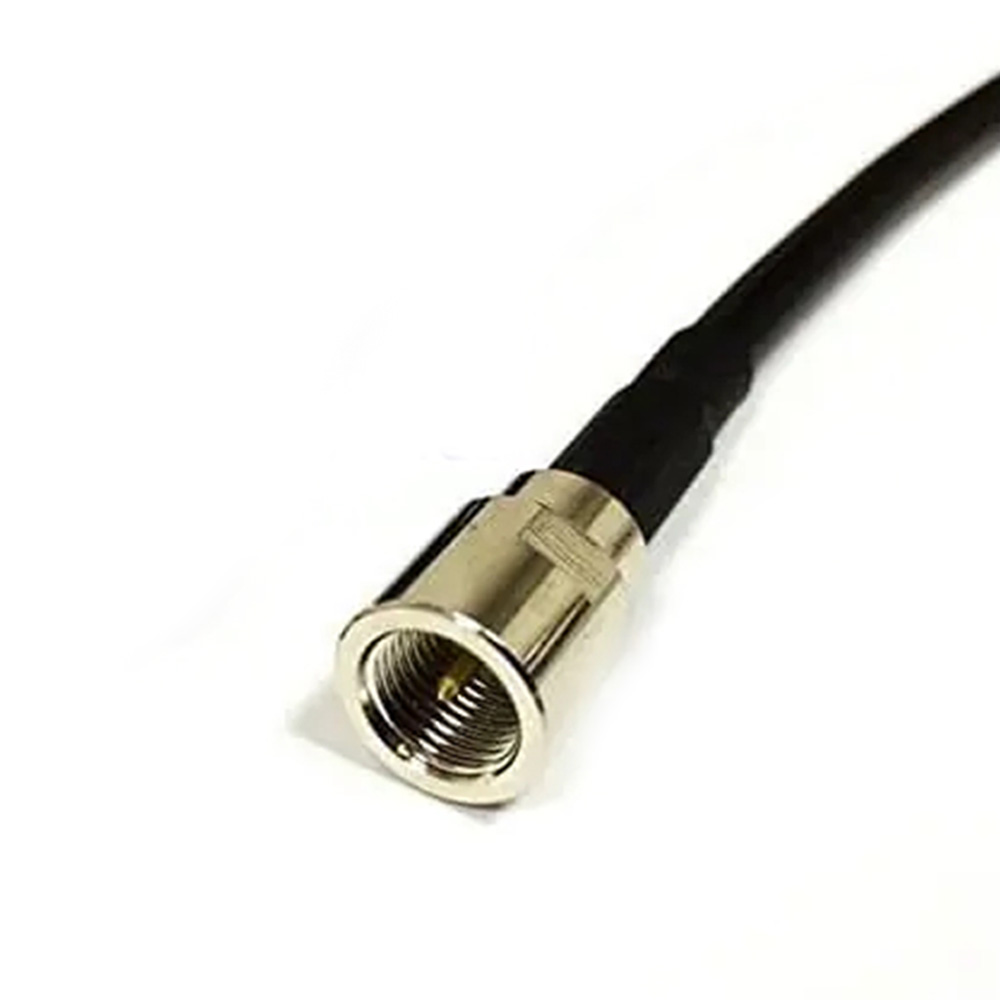
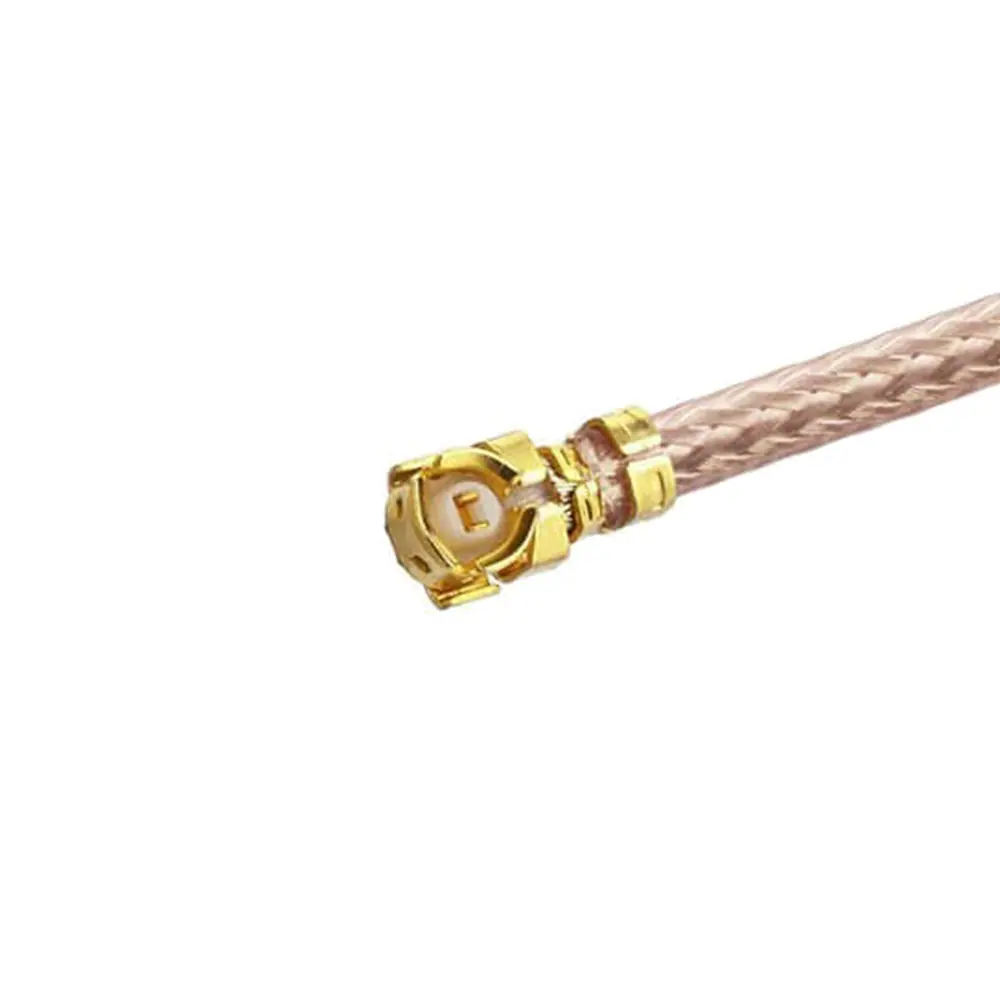
RF cable assemblies typically consist of RF coaxial connectors and coaxial cables, with the connectors mechanically attached to the cables. This design not only ensures the reliability and stability of signal transmission but also adapts to various complex communication environments and application scenarios.
When designing and selecting RF cable assemblies, engineers need to consider multiple factors, including frequency range, impedance matching, power loss, environmental tolerance, and ease of installation and maintenance. Different applications require different types of RF cable assemblies. For example, low-loss cables are suitable for long-distance high-frequency signal transmission, while flexible cables perform well in scenarios that require bending and have space constraints.
With the proliferation of emerging technologies such as 5G and the Internet of Things (IoT), the demand for high-frequency, low-loss, and high-efficiency RF cable assemblies is continuously increasing. In the future, RF cable assemblies will continue to play a key role in driving the development of communication technology.
Differences Between RF Cables and Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables consist of an inner conductor, an insulating layer, a metallic shield (usually braided or foil), and an outer insulating layer. This design minimizes interference and signal loss. Coaxial cables are primarily used for transmitting high-frequency electrical signals with minimal loss and are commonly found in applications like television, internet connections, and other situations where signal integrity is crucial. There are various types of coaxial cables, such as RG-6, RG-58, and RG-59, each designed for specific frequencies and applications.
RF cables are used to transmit radio frequency signals, which range from 3 kHz to 300 GHz. While RF cables can be coaxial, not all RF cables are coaxial. The term “RF cable” broadly refers to any cable used for transmitting RF signals, including coaxial cables, twisted pairs, and even waveguides in some cases. RF cables come in various forms depending on the specific frequency and application, and some may include specialized connectors like SMA, BNC, or N-type connectors.

The key difference is that while all coaxial cables can be used as RF cables, not all RF cables are coaxial. RF cables are a broader category that includes coaxial cables as well as other types of transmission lines. Coaxial cables are specifically designed with consistent impedance to minimize signal loss, making them ideal for RF applications, but they are just one type of RF cable.
Components of RF Cables
RF cables typically consist of the following main parts:

Inner Conductor: A metal wire or filament made of conductive materials such as copper or aluminum, used to transmit electrical signals.
Insulator: An insulating material wrapped around the inner conductor, such as polyethylene (PE) or polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), used to isolate the inner conductor and support the outer conductor.
Outer Conductor: A metal layer outside the insulator, usually made of a braided wire mesh or metal foil, used to shield the inner conductor from external electromagnetic interference and provide mechanical protection.
Jacket: A protective layer covering the outer conductor, typically made of wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or polyethylene (PE), used to protect the cable from environmental influences and mechanical damage.
These components work together to form a complete RF cable for transmitting high-frequency signals in RF systems.