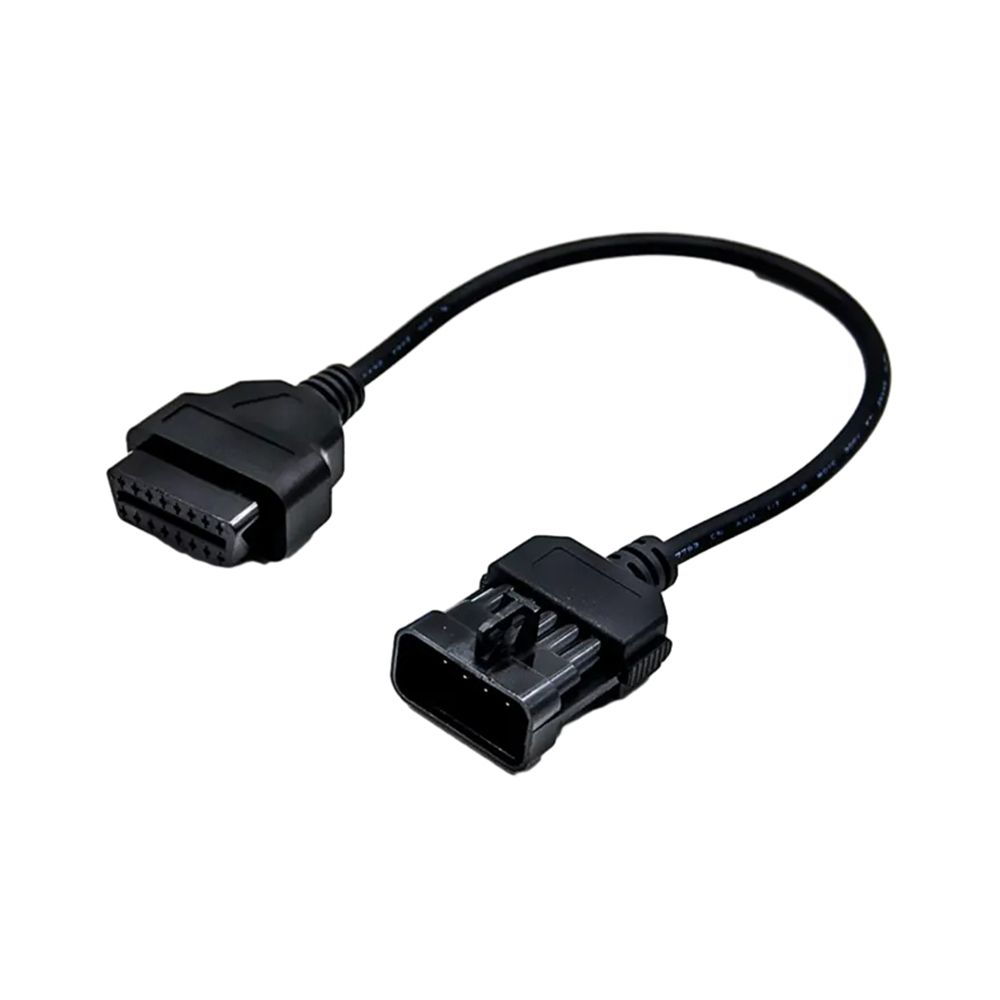
Products
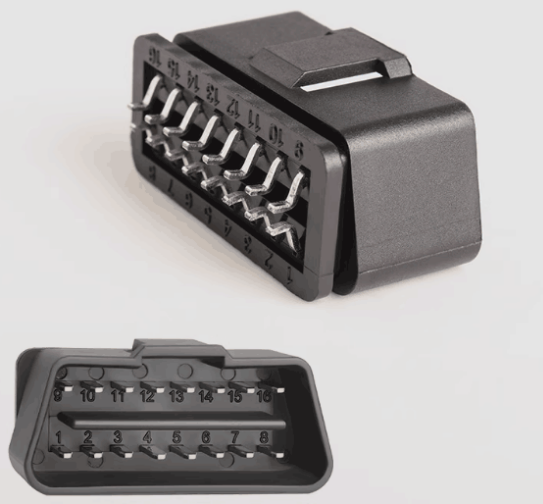
What is an OBD Connector?
The OBD connector, namely On-Board Diagnostics connector, is a crucial component in the automotive electronic system. It serves as an interface device that connects the vehicle’s Electronic Control Unit (ECU) and external diagnostic equipment, acting as a bridge for data interaction between the vehicle and external diagnostic tools.
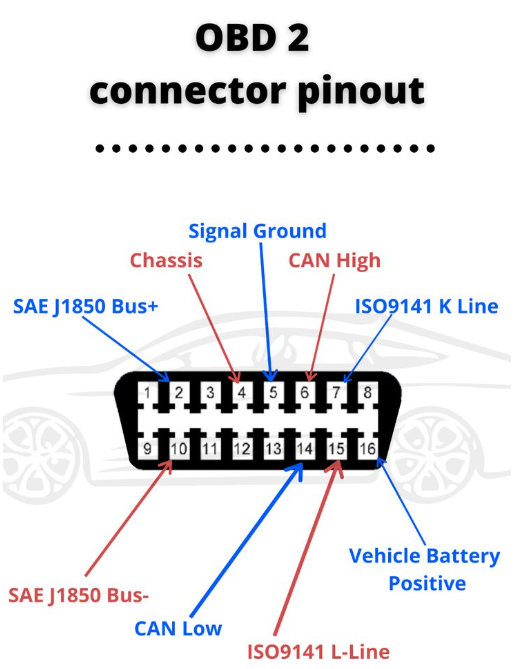
It typically takes the form of a standard 16-pin connector, which is generally rectangular in shape, with specific dimensions and shape specifications. This ensures a certain degree of universality and compatibility across different vehicle models.
Each of the 16 pins has a specific function and definition. For example, some pins are used for power supply, some for data transmission, and some for grounding. These pins are connected to various electronic control modules and sensors within the vehicle through internal circuits, enabling the transmission of data and the exchange of commands.
It is usually located inside the vehicle’s cab. Common positions include under the steering wheel, near the dashboard, or below the center console, which are convenient for operation. In some vehicle models, an OBD connector may also be set in the engine compartment to facilitate maintenance personnel in connecting diagnostic equipment when inspecting engine-related issues.
Its shape, pin definitions, and communication protocols all comply with international standards, such as ISO 15031-3 and SAE J1962. These standards guarantee excellent compatibility and interoperability between vehicles produced by different automakers and diagnostic equipment of different brands and types.
What are the functions of OBD?

Establishing Communication Connection: The OBD connector serves as a bridge between the vehicle’s electronic control system and external diagnostic devices. It can set up a communication channel between various electronic control units of the vehicle, such as the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) and the Engine Control Unit (ECU), and devices like diagnostic testers and scanning tools. This enables maintenance personnel or vehicle owners to obtain information inside the vehicle through external devices.
Data Transmission: On one hand, it can transmit the real-time operating data of various systems and components of the vehicle, such as engine speed, vehicle speed, coolant temperature, oxygen sensor data, etc., from the vehicle’s electronic control units to external diagnostic devices for display and analysis. On the other hand, it can also transmit commands or configuration information sent by external devices to the vehicle’s electronic control units, enabling the setting or testing of certain functions of the vehicle.
Fault Diagnosis: When a vehicle malfunctions, the electronic control unit will generate corresponding fault codes. The OBD connector can transmit these fault codes to the diagnostic device. Maintenance personnel can then quickly locate the system or component where the fault lies according to the fault codes and determine the nature and approximate scope of the fault, improving the efficiency of fault detection and repair.
Software Update and Programming: When the vehicle undergoes software upgrades, control unit programming, or configuration parameter adjustments, the OBD connector can act as a data transmission channel, allowing new software programs or configuration information to be smoothly transferred from external devices to the vehicle’s electronic control units, achieving the update and optimization of the vehicle system.
Emission Detection: In scenarios such as environmental protection inspections or vehicle annual inspections, the detection device can read the vehicle’s emission-related data through the OBD connector, such as the content of various pollutants in the exhaust gas and the working status of the emission control system, to determine whether the vehicle meets the environmental protection emission standards.
Vehicle Performance Monitoring and Optimization: Vehicle owners or professionals can use devices connected to the OBD connector to monitor the vehicle’s performance data in real-time and understand the vehicle’s operating status. Based on this data, the vehicle’s performance can be tuned, such as optimizing the engine’s ignition timing and adjusting the fuel injection amount, etc., to improve the vehicle’s power performance and fuel economy.
Data Recording and Analysis: The data obtained through the OBD connector can be recorded for subsequent analysis. For example, fleet managers can analyze the vehicle’s driving data to understand the vehicle’s usage situation, drivers’ driving habits, etc., for better management and scheduling. Automobile manufacturers can collect data from a large number of vehicles for product quality improvement and after-sales service optimization.